Glycaemic care inpatient (For non critically ill)
Glycaemic care inpatient (For non critically ill)
Source: Practical Guide To Inpatient Glycemic Care 2020, MEMS MOH
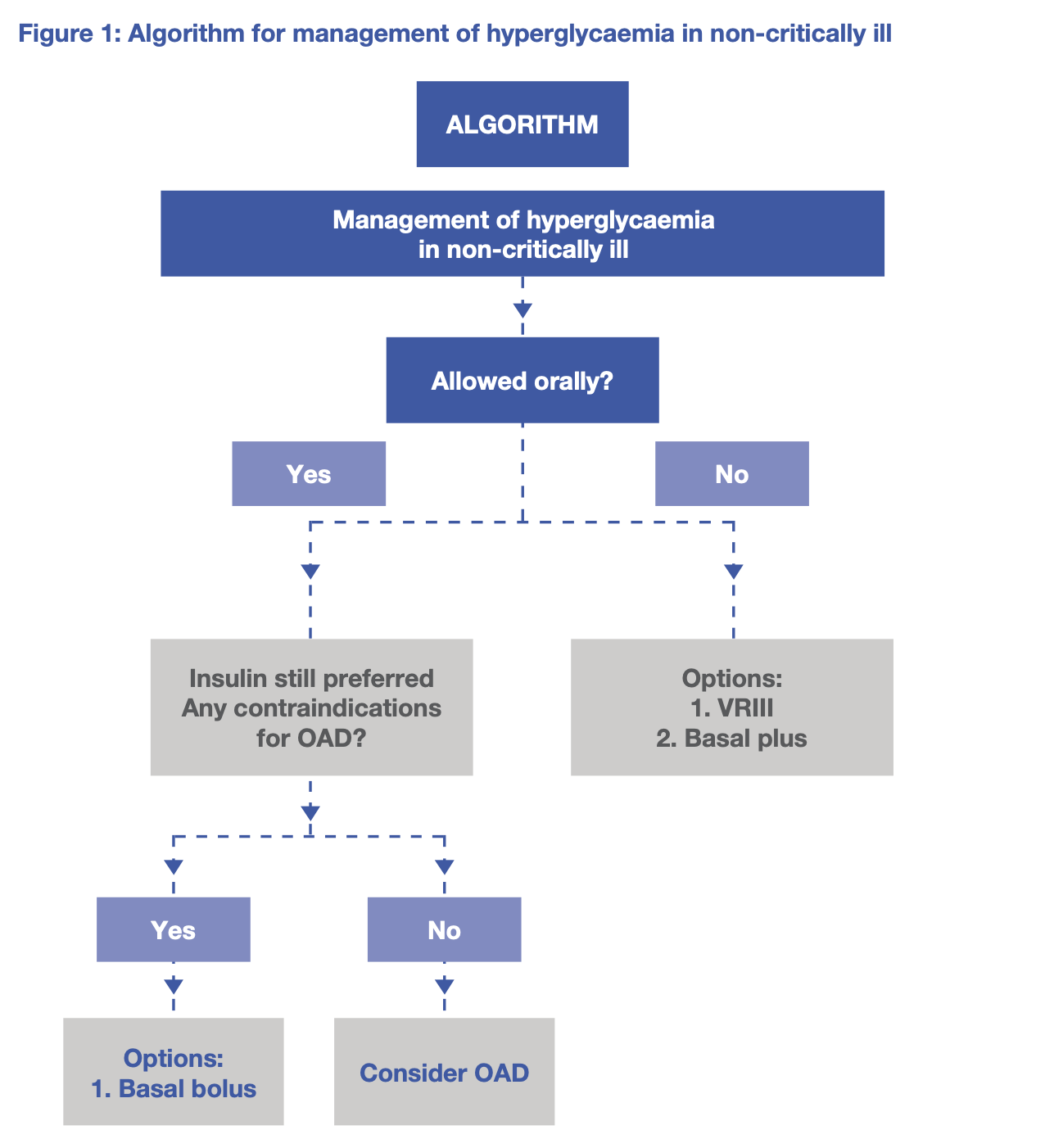
Introduction
Insulin is the preferred choice for pharmacological therapy for hospitalised patients
In hospitalised patients,
- Hyperglycaemia is defined as BG > 7.8mmol/L
- Hypoglycaemia is defined as BG < 4.0mmol/L
- HbA1c ≥ 6.3% suggests pre-existing diabetes
Recommendations
- Inpatient glycaemic target, ICU and non-ICU is 7.8 - 10mmol/L
- Insulin should be initiated once BG persistently ≥ 10mmol/L
- In selected patients, stricter target of 6.1 - 7.8mmol/L can be considered while avoiding hypoglycaemia
Ways of lowering BG
- Variable rate intravenous insulin infusion (VRIII) - NBM (may cause iatrogenic hypokalaemia)
- Scheduled subcutaneous insulin – basal bolus/prandial regimen - Tolerating oraly (efective and no danger iatrogenic hypokalaemia)
- Scheduled subcutaneous insulin – basal plus regimen - NBM (no danger iatrogenic hypokalaemia)
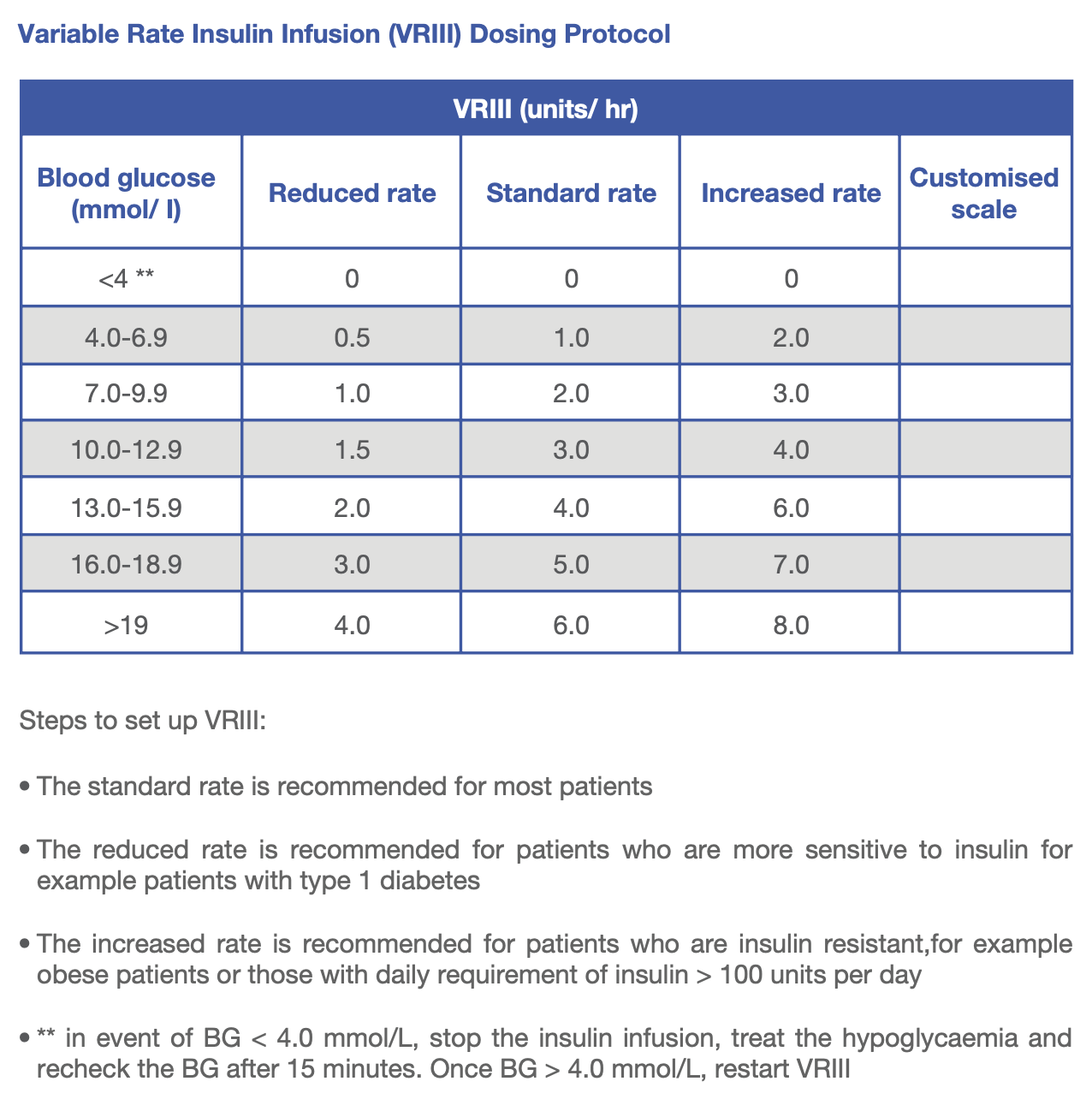
Variable rate intravenous insulin infusion (VRIII)
- for NBM patient
- dose as per VRIII Dosing Protocol (Sliding scale table)
- initially use the standard rate of the scale
Adjustment of scale when
- BG persistently >10mmol/L (on 2 readings) (switch to higher scale)
- The initial BG is >20mmol/L and not falling by 3-5 mmol/L/hour (switch to higher scale)
- BG control is too tight (4-6 mmol/L) or episode of hypoglycaemia, (either switch to a lower scale or increase dextrose in drip).
How to endorse (Example)
- 50 units of human rapid acting insulin is drawn up an added to 49.5 ml of sodium chloride in a 50 ml syringe and mixed thoroughly (1 unit insulin = 1 ml)
1
2
IVI Actrapid 50 units in 50 mL NS, 2 mL/hr
IVI Actrapid 50 units in 50 mL NS per sliding scale
Scheduled subcutaneous insulin - basal bolus/prandial regimen
- once tolerating orally
- dose as per body weight (Total daily dose table)
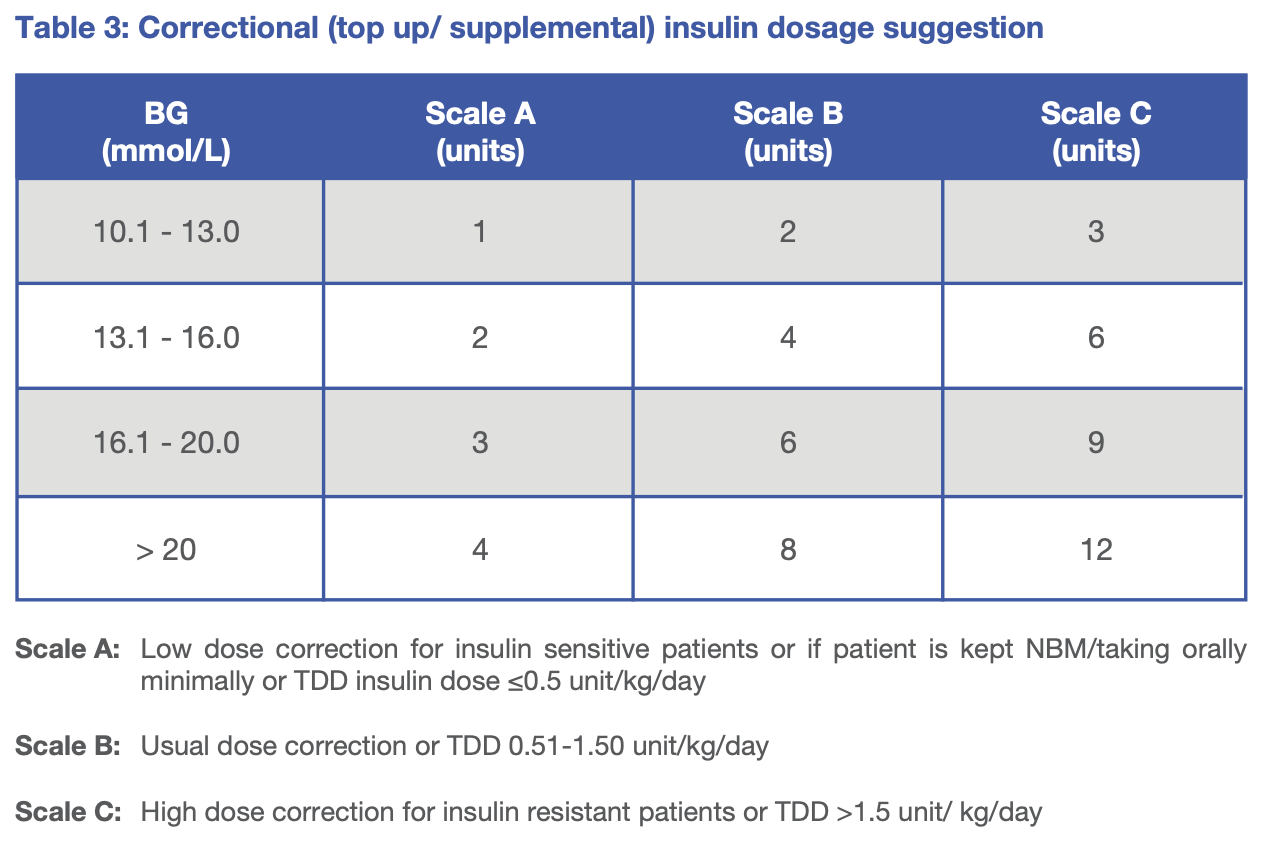
- correction doses (Top up scale table) can be given (only for fast acting insulin) if pre-meal or in between meal BG is elevated/not at target
- 1 basal, 1-3 bolus (for meal) and correction dose
- Total daily dose (TDD) is divided into 50% basal and 50% prandial insulin.
How to endorse (Example)
- Elderly, 60 kg
- TDD = 0.3 U/kg/day × 60 kg = 18 units/day
- Basal (50%) = 9 units
- Prandial (50%) = 9 units → 3 units per meal
1
2
S/C Insulatard 9 units ON
S/C Actrapid 3 units TDS, top up scale B
Scheduled subcutaneous insulin – basal plus regimen
- for NBM patient or poor oral intake
- Calculate TDD as in Total Daily Dose
- Administer basal insulin as above
- Give correction dose of short acting insulin 6 hourly using Scale A in Top up scale
- 1 basal and correction dose
How to endorse (Example)
- Elderly, 60 kg
- TDD = 0.3 U/kg/day × 60 kg = 18 units/day
- Basal (50%) = 9 units
- Correction (50%) = 9 units → 2 units per shot
1
2
S/C Insulatard 9 units ON
S/C Actrapid 3 units QID, top up scale A
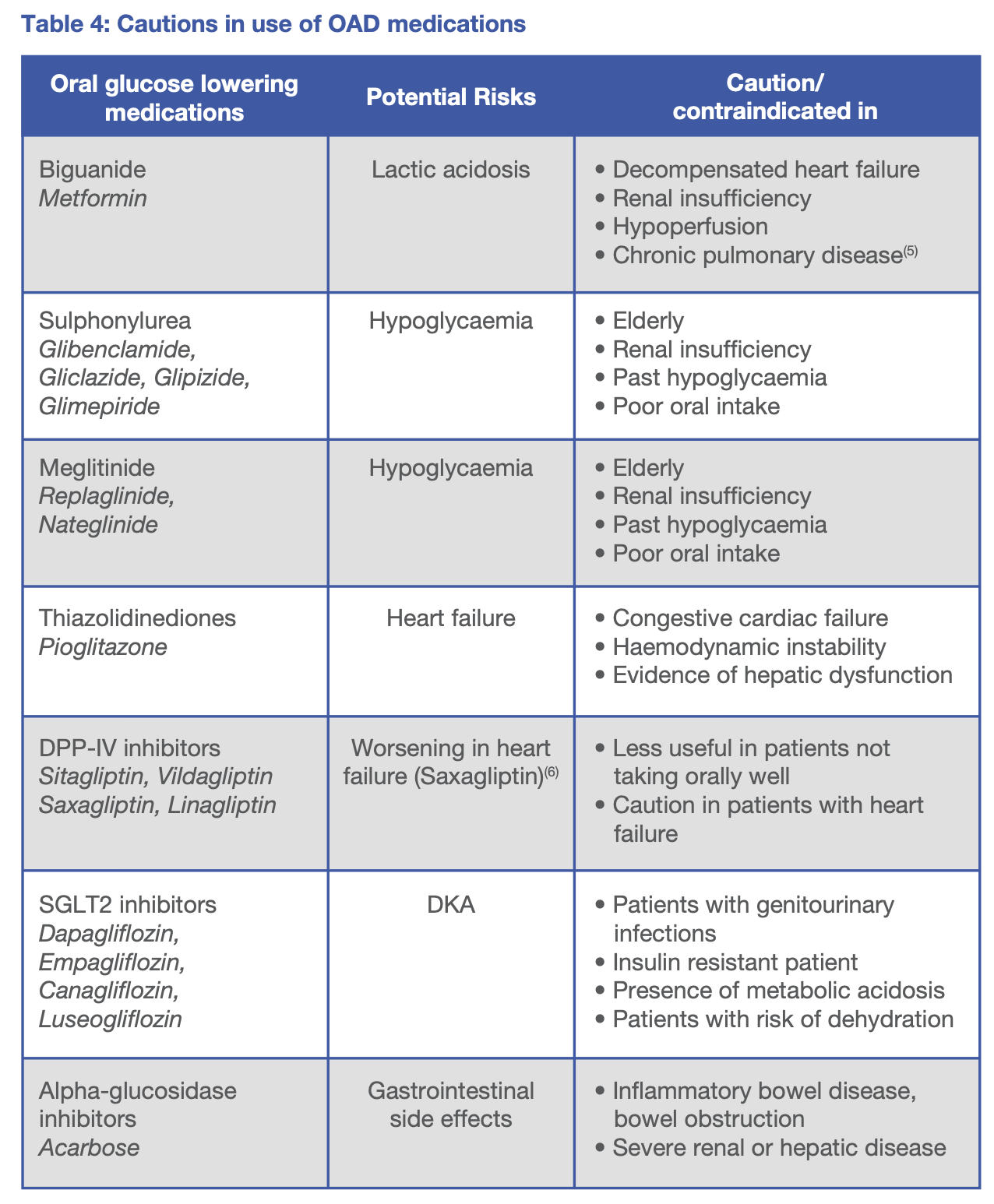
Oral anti-diabetic (OAD) medications
If patient are
- Clinically stable
- Good glycaemic control prior to admission
- Allowed and taking orally well
- No contraindications for use of OAD medications
How to endorse (example)
1
2
3
4
T. Metformin 500mg BD
T. Gliclazide 80mg OD
T. Vildagliptin 50mg BD with T. Metformin 500mg BD
T. Vildagliptin 50mg OD with T. Gliclazide 80mg OD
Pos ini dilesenkan di bawah
CC BY 4.0
oleh penulis.